Comprehensive Insight into the Business of Valse USD: Fake Money, Fake Documents, and Market Dynamics

The global economy operates on trust, transparency, and regulation, but beneath the surface, a clandestine industry thrives around the production and circulation of valse USD. This term, often associated with counterfeit United States Dollars, encapsulates a complex sector intertwined with illegal activities, sophisticated printing techniques, and global networks. In this detailed article, we will dissect the multifaceted world of fake money and fake documents, sketching the landscape, exploring the implications for legitimate businesses, and highlighting the importance of awareness and prevention.
Understanding the Term Valse USD: What Does It Signify?
The phrase valse USD is primarily used within illicit circles, referring to counterfeit or fake US dollars that are intended to deceive. The word valse hints at a French influence, carrying meanings like "false" or "counterfeit," and combined with USD, it points explicitly towards counterfeit American currency. However, this term can also extend metaphorically to encompass counterfeit documents, digital forgeries, and other fraudulent representations in financial and legal sectors.
While valse USD might seem like a straightforward term for counterfeit money, it embodies a deep industry comprising:
- High-quality counterfeit bills crafted with meticulous attention to detail.
- Distribution networks operating both online and offline.
- Fake documents used for various fraudulent activities, including bank account creation, identification theft, or infiltration into legitimate financial channels.
The Evolution of Counterfeit Currency and Fake Documents Industry
The Historical Context and Modern Developments
The printing of counterfeit currency has been part of human history for centuries, evolving from rudimentary notes to highly sophisticated forgeries. Modern valse USD is produced using advanced printing techniques, high-quality paper, and even security features that mimic real bills, such as watermarks, holograms, and microprinting. The rise of digital technology further complicates this landscape, enabling counterfeiters to generate digital forgeries or manipulate images of authentic bills convincingly.
Parallel to physical fake currency, the counterfeit industry also heavily involves the creation of fake documents like passports, driver’s licenses, and identification cards. These are essential tools for criminals to access financial systems, evade law enforcement, or conduct outright fraud on an international scale.
How Does the Valse USD Business Operate?
Supply Chain and Production
The production of valse USD involves several key phases:
- Design and master forgery: Skilled counterfeiters use sophisticated software and printing equipment to replicate the intricate details of genuine currency and documents.
- Printing and manufacturing: Using special paper and inks, the counterfeit bills are printed with high fidelity to genuine bills, often matching security features to fool untrained eyes.
- Distribution channels: The fake currency and documents are then distributed through darknet markets, discreet underground networks, or physical courier services.
Markets and Consumer Base
The clientele for valse USD includes a variety of actors, from petty criminals involved in street-level transactions to organized crime syndicates conducting large-scale operations. Fake documents are sought after for identity theft, financial fraud, or bypassing border controls. The business thrives on secrecy, rapid turnover, and the ability to adapt to detection methods.
Risks and Legal Consequences in the Valse USD and Fake Documents Industry
Engaging in this clandestine market carries significant risks—legal penalties, financial loss, and damage to reputation. Governments worldwide have dedicated law enforcement units to combat counterfeit currency and document-related crimes:
- Severe penalties: Including lengthy imprisonments, hefty fines, and asset confiscation.
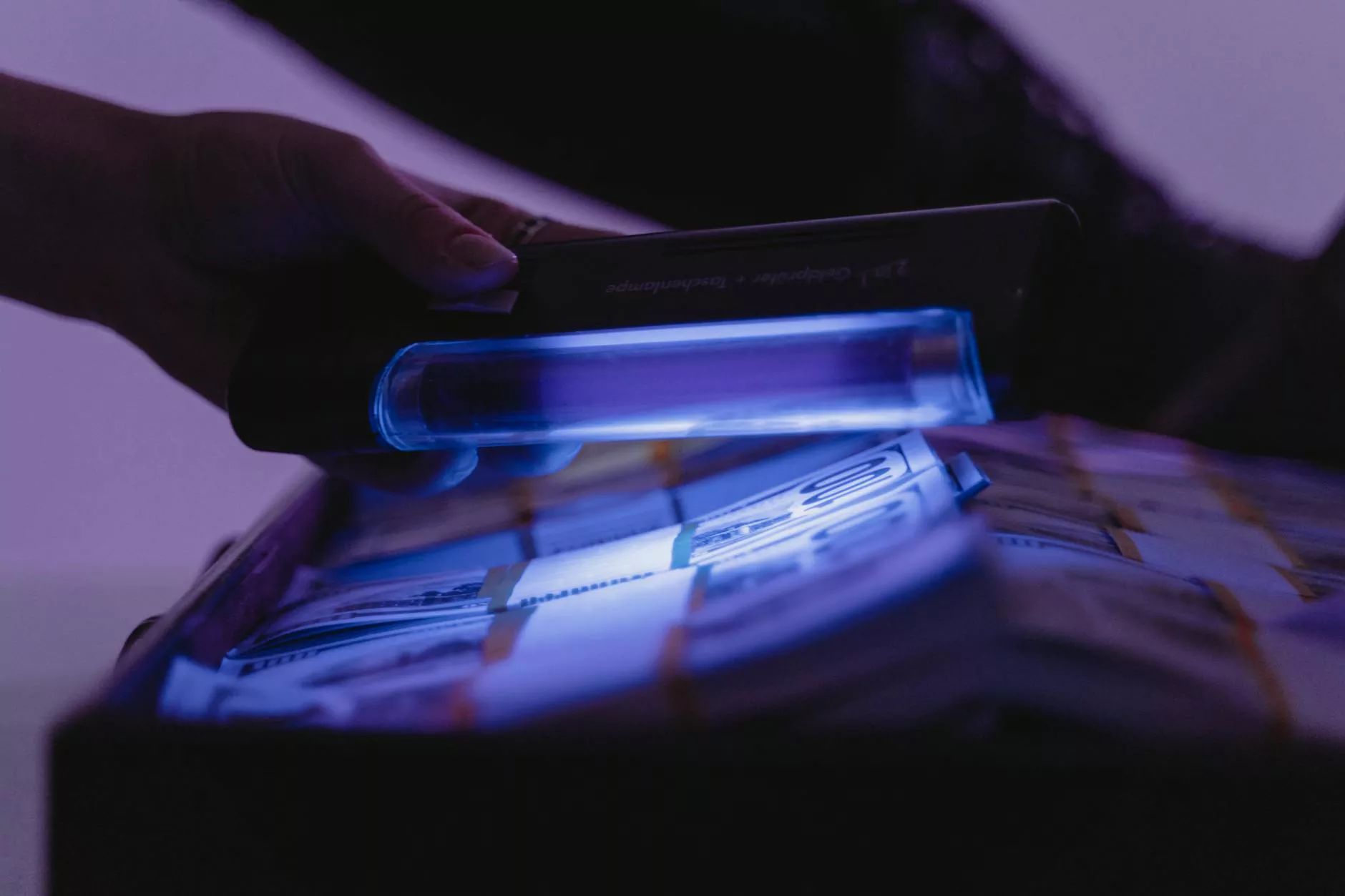
- Technological countermeasures: Banks and authorities now use advanced detection devices that analyze magnetic strips, holograms, UV features, and microprinting.
- Increasing sophistication: As counterfeiters improve their techniques, law enforcement continually updates its detection capabilities, making it a constant cat-and-mouse game.
Understanding the Impact of Fake Money and Documents on Businesses
Economic and Reputational Damage
Businesses that unknowingly accept valse USD face not only financial loss but also potential legal problems and damage to customer trust. Fake documents used for fraudulent activities can lead to identity theft, financial scams, and security breaches, risking long-term harm for both individuals and companies.
The Role of Businesses in Combating Fake Money and Documents
Companies must stay vigilant by implementing rigorous verification procedures, investing in detection technology, and training personnel on how to identify counterfeit items. Collaborations with law enforcement agencies and industry groups can strengthen the understanding of emerging threats and best practices.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Manufacturing, distributing, or even inadvertently possessing valse USD and fake documents is illegal across most jurisdictions. Engaging in such activities exposes individuals and companies to criminal charges and civil liabilities. Ethically, businesses should promote transparency, authenticity, and trust, adhering to regulatory standards and fostering a responsible marketplace.
How to Protect Your Business from the Threats of Valse USD and Fake Documents
Implementing Effective Security Measures
- Use advanced currency detection devices that analyze banknotes for security features like microprinting, UV features, and holograms.
- Educate staff regularly on how to detect counterfeit bills and fraudulent documents.
- Establish strict verification protocols for large transactions and high-risk customers.
- Partner with trusted security vendors and law enforcement agencies for updates on counterfeit trends.
- Maintain a clean digital footprint by verifying identities using official databases and secure methods.
Adopting Best Practices for Prevention
- Develop clear policies for handling suspicious currency or documents.
- Regularly audit financial transactions and records.
- Utilize software solutions capable of analyzing images and detecting forgeries.
- Engage in ongoing staff training on emerging counterfeit techniques.
- Maintain open lines of communication with authorities for reporting and receiving alerts on counterfeit operations.
The Future of Valse USD and Counterfeit Documents Industry
With technological advances, the counterfeit industry is expected to become more sophisticated and harder to detect. Innovations such as blockchain-based verification, biometric authentication, and artificial intelligence will play pivotal roles in combatting fake money and documents.
Conversely, counterfeiters will continue to adopt these technologies to stay ahead, making ongoing vigilance paramount. Businesses, governments, and consumers must all adapt to an evolving landscape to safeguard their interests and uphold the integrity of financial and legal systems.
Conclusion: The Need for Vigilance and Ethical Practices
The valse USD industry, with its extensive network of fake money and documents, poses significant challenges, but awareness, technological defense, and ethical standards can mitigate its impact. Understanding the complexities, risks, and legal frameworks involved is essential for any business operating in today’s interconnected economy.
By implementing comprehensive security measures and fostering a culture of integrity, companies can protect themselves against counterfeit threats, uphold their reputation, and contribute to a safer financial environment globally.
Remember, vigilance and responsibility are the best defenses against the shadowy world of valse USD and counterfeit documentation. Staying informed and proactive is key to outpacing counterfeiters and maintaining trust in your business operations.